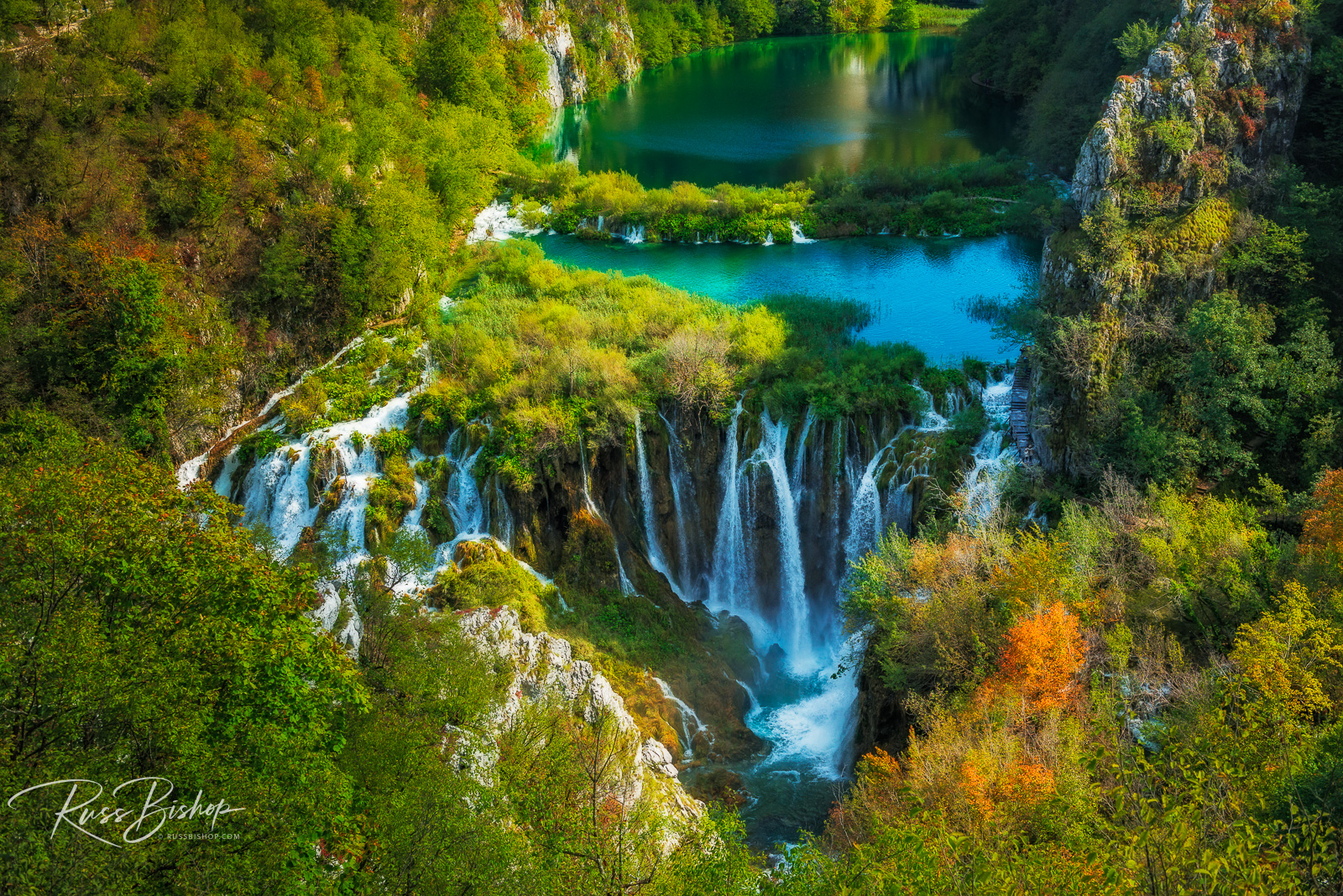
The mesmerizing waterfalls at Plitvice Lakes National Park are renowned for their unique colors, ranging from azure to green and blue. The waters are fed from underground Karst formations, and the colors change constantly throughout the day depending on the quantity of minerals and organisms in the water and the angle of sunlight.
Delicate travertine dams separate the 16 lakes that are visible on the surface, creating a unique ecosystem between each body of water. Formed as plants and bacteria in the water interact with the air, these barriers grow at a rate of 1 centimeter a year and continue to shape and form the myriad cascades the park is famous for.
Established in 1949, Plitvice Lakes is one of the oldest national parks in Europe and was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1979. Croatia is a beautiful country with a rich and colorful past, and as one of the newest members of the European Union its friendly atmosphere and gorgeous scenery make this an ideal addition to any European adventure.
©Russ Bishop/All Rights Reserved