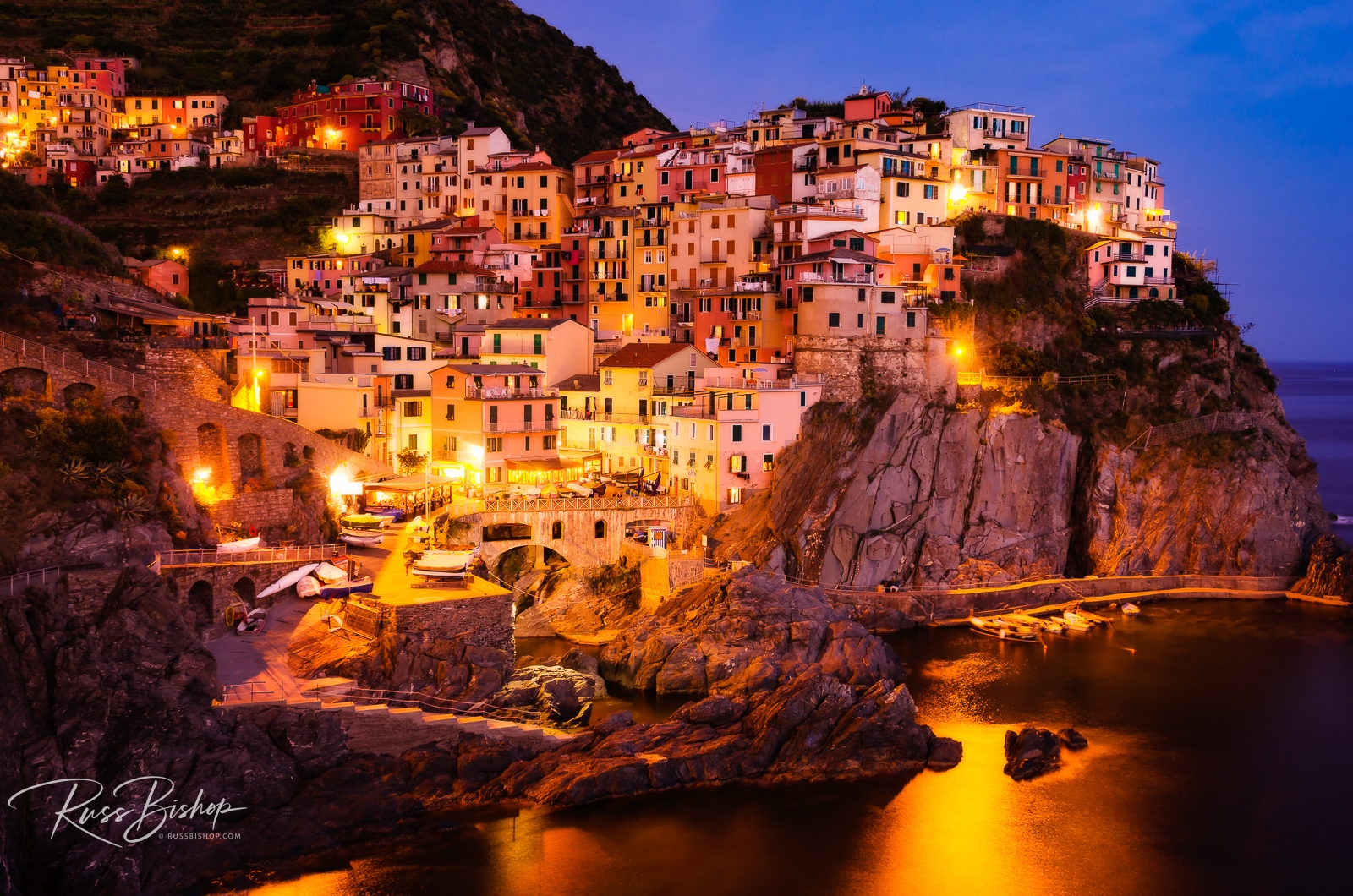
Hanging cliff-side along the Italian Riviera, the sleepy hamlets of Cinque Terre are a traveler’s paradise. Set aside as Italy’s first national park in 1999, these five quaint fishing villages (Italian for “Five Lands”) dot a magical strip of coastline accessible only by boat, train or foot.
Riomaggiore, Manarola, Vernazza and Monterosso are all right on the water, while Corniglia sits atop a promontory surrounded by vineyards high above the Ligurian Sea. The only way to reach the latter is via the Lardarina, an intimidating 377-step brick stairway, or the park service shuttle bus from the train station. Cars were banned in all of the villages years ago, which has helped retain the old world feel that has existed here for centuries.
Walking is very popular in the region especially on the main coastal paths where centuries-old terraces cling to the rugged cliffs above the sea. The Sentiero Azzurro (or Blue Path) is the primary trail that connects the five villages and offers sweeping views of the coastline. Harbors filled with colorful fishing boats and trattorias serving local seafood specialties and Liguria’s famous pesto are the reward at the end of the journey.
Frequent trains link all five villages, and you can purchase an all day pass that also includes a hiking pass at the tourist information offices located in each town. A more expensive, but equally scenic option are the boats that travel along the coast several times throughout the day.
The towns of Cinque Terre date from the early medieval period, and the area was designated a UNESCO World Heritage site in 1997. Though no longer the undiscovered find it once was, Cinque Terre’s charm and classic Italian hospitality still retain the feel of old Italy and make this a prime stop on any European adventure.
©Russ Bishop/All Rights Reserved